Blockchains depend on consensus mechanisms to confirm transactions, however why does it matter if a community is proof-of-work (PoW) or proof-of-stake (PoS)? On this information, we’ll break down PoW vs. PoS in easy phrases, explaining how every technique secures the blockchain whereas addressing the professionals and cons and options of every. Right here’s what to know in 2024.
On this information:
- What’s proof-of-work (PoW)?
- What’s proof-of-stake (PoS)?
- Proof-of-work vs. proof-of-stake: Comparability
- Challenges related to PoW
- Challenges related to PoS
- Which consensus is best: PoS or PoW?
- Regularly requested questions
What’s proof-of-work (PoW)?
Proof-of-work (PoW) is a consensus mechanism the place miners use computational energy to resolve advanced mathematical puzzles and validate transactions on a blockchain. This course of ensures the community is safe and decentralized via the competitors of miners.
Key traits of PoW
- Mining-based validation: Miners compete to resolve cryptographic puzzles, with the winner attending to validate a block and obtain rewards.
- Vitality-intensive: Similar to an enormous puzzle competitors requires power, PoW makes use of loads of computational energy, making it energy-intensive.
- Safety via problem: The complexity of the puzzles makes it very tough for anybody to tamper with the community. Any modifications would require re-solving all earlier puzzles, which is virtually inconceivable.
How PoW ensures safety and decentralization
PoW supplies safety by making it extraordinarily expensive to attempt to assault or manipulate the community. The assets wanted to cheat are so excessive that it’s not well worth the effort. On the similar time, PoW permits anybody with the precise {hardware} to take part in mining, making certain no single entity controls the community.
Examples of blockchains utilizing PoW
- Bitcoin: The primary cryptocurrency to implement PoW, Bitcoin’s decentralized community depends on miners to safe the blockchain.
- Litecoin: A fork of Bitcoin, Litecoin makes use of PoW however provides sooner transaction occasions, making it extra appropriate for smaller, on a regular basis transactions.
What’s proof-of-stake (PoS)?
Proof-of-stake (PoS) is a consensus mechanism the place validators are chosen to create new blocks primarily based on the quantity of cryptocurrency they maintain and are keen to “stake” as collateral. This technique reduces the necessity for energy-intensive computations and will increase community effectivity.
Key traits of PoS
- Staking replaces mining: As a substitute of miners, PoS makes use of validators who lock up (or stake) their cash for an opportunity to validate blocks.
- Vitality effectivity: Since PoS doesn’t depend on heavy computation, it consumes considerably much less power than PoW.
- Validator choice primarily based on stake: Validators are chosen primarily based on what number of cash they’ve staked, which incentivizes holding and securing the community.
Staking and validator choice course of
In PoS, validators lock up a portion of their cryptocurrency as collateral. When chosen, they validate new transactions and add them to the blockchain. In the event that they act dishonestly, their staked cash will be slashed (misplaced), making certain contributors comply with the principles. This technique favors those that have a big stake but additionally permits smaller holders to take part.
Examples of blockchains utilizing PoS
- Cardano: A number one PoS blockchain identified for its research-driven method, Cardano emphasizes safety and sustainability via staking.
- Ethereum: After its transition from PoW in 2022, Ethereum now makes use of PoS, tremendously rising its power effectivity and scalability.
Proof-of-work vs. proof-of-stake: Comparability
Whereas the variations can at all times be detailed, here’s a fast desk to your reference, which could make it easier to make higher sense of how every works:
Challenges related to PoW
Whereas proof-of-work (PoW) is well known for its safety and decentralization, it comes with vital challenges. Its power consumption, centralization dangers, and gradual transaction speeds pose limitations for scalability.
Excessive power consumption
One in all PoW’s most talked-about drawbacks is its environmental influence. The power required to resolve cryptographic puzzles is very large, resulting in issues about sustainability. This has prompted debates about greener alternate options in blockchain know-how.
Bitcoin’s huge transactional, belief, and safety benefits are offset by the actively resource-intensive design of its transaction verification course of, which now compromises our capability to outlive in a climate-dependent world.
Truby, J. (2018). Decarbonizing Bitcoin: Science Direct
The chart under demonstrates the change in Ethereum’s power consumption after transferring from a PoW consensus mechanism to PoS.
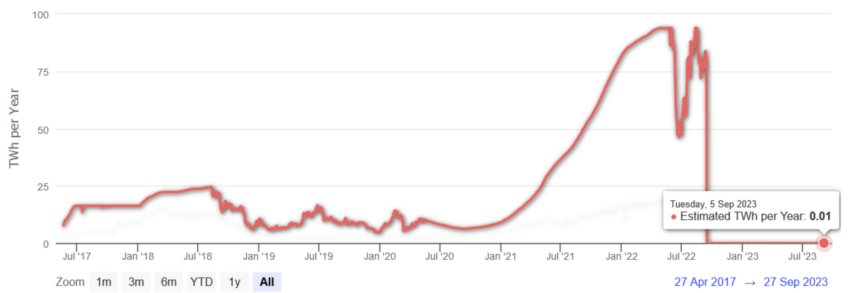
Ethereum power consumption: Limenet.tech
Centralization dangers attributable to mining swimming pools
As mining turns into extra aggressive and hardware-intensive, smaller miners battle to compete. This has led to the rise of mining swimming pools — teams of miners who mix their assets to resolve puzzles collectively. Whereas this makes mining extra environment friendly, it additionally dangers centralizing energy within the fingers of some massive swimming pools, which may undermine the decentralization precept of PoW.
Slower transaction occasions
PoW networks like Bitcoin course of transactions at a slower tempo in comparison with newer consensus mechanisms. As miners want time to resolve every puzzle, block technology can take longer, inflicting delays in transaction validation, particularly during times of excessive community visitors.
Challenges related to PoS
Proof-of-stake (PoS) is praised for being energy-efficient and scalable, but it surely faces its personal set of challenges. These embrace:
- Dangers of centralization
- Potential safety vulnerabilities
- The complexity of staking
Dangers of centralization attributable to wealth focus
In PoS programs, validators with bigger quantities of staked cryptocurrency have a better probability of being chosen to validate blocks. This will result in a state of affairs the place a small group of rich contributors controls a good portion of the community, elevating issues about centralization.
Safety issues (long-range assaults, slashing dangers)
Whereas PoS is mostly thought-about safe, it has its personal vulnerabilities. One such danger is a long-range assault, the place an attacker rewrites historical past from far again within the blockchain.
To mitigate this, PoS programs implement penalties (slashing) for validators who act dishonestly. Nonetheless, there’s a danger that trustworthy validators is likely to be penalized accidentally, resulting in the potential lack of staked cash.
Complexity of the staking course of
Staking could be a difficult course of, particularly for newbies. Validators want to grasp how a lot to stake, handle the dangers of slashing, and keep on-line to take care of their function within the community. This complexity might discourage smaller holders from collaborating, probably leaving the system within the fingers of extra skilled or wealthier customers.
As of 2024, a number of hybrid fashions are being explored, combining elements of each PoW and PoS. For instance, tasks like Kadena use PoW for safety and PoS for governance to strike a stability between safety and power effectivity.
Which consensus is best: PoS or PoW?
There isn’t a transparent winner on this proof-of-work vs. proof-of-stake dialogue; every has its strengths and weaknesses relying on the use case. Nonetheless, as blockchain know-how matures, PoS is gaining extra consideration for its power effectivity, sustainability, and scalability, whereas PoW stays trusted for its excessive degree of safety.
Whereas many new chains select to embolden greener credentials with PoS, the standing of the unique and hottest blockchain, Bitcoin, as PoW ensures that the extra energy-intensive consensus mechanism will stay related in the long run.



